The Alpine Fault is due for a powerful earthquake in New Zealand. Map via Wikicommon
By Strange Sounds
Pressure is building along the Alpine Fault, one of the most active fault lines in the world and New Zealand is in a race to be ready. Latest results show that a great earthquake, one of the biggest in New Zealand’s modern history, is due.
Description of the Alpine Fault
For millions of years, the shifting Australian and Pacific tectonic plates below have been pushing together, buckling, breaking the ground and molding this mountain range.
Where the two plates meet on land is known as the Alpine Fault, a 850-kilometer seam in the Earth’s crust that traces an almost perfect path along the western foothills of the alps.

Near Milford Sound, the fault has left visible scars that cut through the landscape. It’s a familiar sight all along the west coast. To the north, at Gaunt Creek, the fault line extrudes from the ground. It’s one of the few places on earth where you can touch a fault. Picture by ABC News
On average, the plates move 2-3 centimeters a year relative to each other. It may sound slow, but in geological time that’s a blistering pace. But instead of being gradual movement, the plates move several meters at a time every few hundred years.
Scientists believe these plates are due to move again and when it happens it will trigger a powerful earthquake.
Timeline of earthquakes along the Alpine Fault
In studying the Alpine Fault, scientists have created a timeline of its history and they know it makes very big shifts, on average, about every 300 years.
It’s complex science that dates the last magnitude-8 earthquake along the fault line to the year 1717.
Simple maths tells us it’s been more than 300 years since then.
So, what kind of earthquake is next for the Alpine Fault?
That’s the question senior lecturer in physical geography at the Victoria University of Wellington Jamie Howarth and his team recently set out to answer.
The team developed the richest record yet of the Alpine Fault’s history and found a pattern, one that helps them reliably forecast what’s to come.
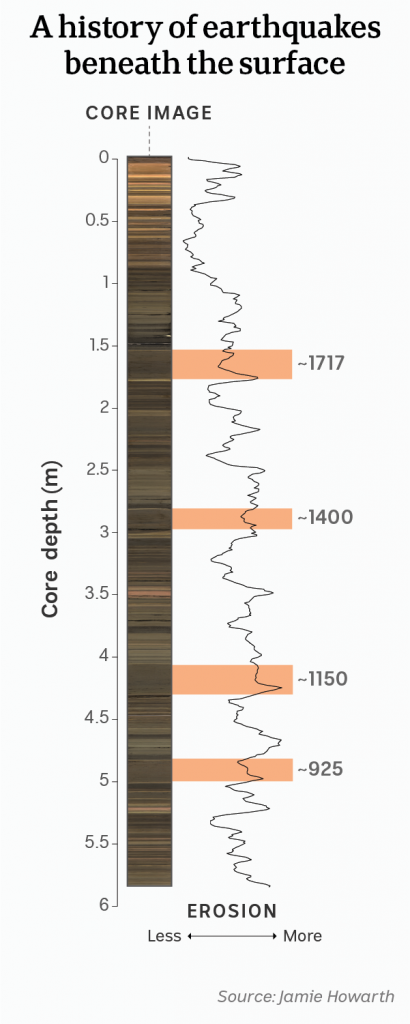
The research team drilled down six meters and extracted a cross-section of the lake bed, revealing a literal line-by-line snapshot of its history.
“[It] gets us back a few thousand years into the past and then we can read that record like a book, identify those past earthquakes and date them,” Jamie said.
In this sample, the red zones represent each major Alpine Fault earthquake back to the year 925AD.